
-
$200 + 2% Cash Back !
-
Annual Fee 0$
-
Unlimited 2% Cash Rewards on purchases
-
0% intro APR for 15 months
-
24/7 Visa Signature® Concierge ❤️

-
$300 + 1.5%-6.5% Cash Back !
-
Annual Fee 0$
-
0% intro APR for 15 months
-
No minimum to redeem for cash back
-
Reco. Credit Score : 690-850

-
$200 + 1%-10% Cash Back !
-
Annual Fee 0$
-
0% intro APR for 15 months
-
3% cash back : dining, streaming, grocery stores, entertainment...
-
Reco. Credit Score : 690-850

-
75 000 Bonus Miles !
-
Annual Fee 95$
-
Flexible rewards redemption
-
Reco. Credit Score : 690-850
-
XXXXX

-
60 000 Bonus Points !
-
Annual Fee 95$
-
Rewards Rate 1x-5x
-
Flexible Rewards Redemption
-
Reco. Credit Score : 690-850

-
$250 + 1%-6% Cash Back !
-
$0 annual fee (1st year), then $95
-
0% intro APR for 12 months
-
Cash rewards
-
Reco. Credit Score : 690-850

-
1-5% Cash Back !
-
$0 annual fee
-
Redeem your Rewards for Cash Anytime
-
Earn 5% Cash Back on Everyday Purchases
-
Reco. Credit Score : 690-850
Are you new to the world of credit cards and feeling a bit lost ? No problem, here's a quick and simple guide to everything you need to know about credit cards to make the right choice !
✅ How Do Credit Cards Work ?
Using a credit card allows you to purchase goods or services, either in-person or online. When you apply for and receive approval for a credit card, you're granted a line of credit determined by factors such as your credit score and income.
One of the primary benefits of using a credit card compared to cash or debit card payments is that it acts like a short-term loan. This means you have until the end of the credit card billing cycle, also referred to as the grace period, to pay off what you've spent.
Some cards also offer cash-back or travel rewards, along with additional benefits like purchase and travel insurance. However, if you don't pay off the full amount spent by the end of this period, you will accumulate interest on your purchases, which can become costly over time.
It's advised not to take the choice of credit card lightly. Your lifestyle, income, credit line needs, and reward preferences can change. Additionally, credit cards may adjust their benefits, reward rates, and fees.
The concept behind credit cards is straightforward: using a credit card means borrowing money to make a purchase. Later, you must repay what you've borrowed. If you opt to pay back the amount over an extended period instead of paying in full when your credit card statement arrives, you'll be charged interest. This fundamental principle underpins the credit card industry.
A typical credit card transaction proceeds as follows:- You make your purchase by swiping your card at a register or entering your card details online.
- The purchase is authorized after the credit card company verifies the card is valid for the transaction amount.
- The merchant is paid by the bank that issued your credit card, which sends the transaction's funds.
- You then repay the bank for the purchase, which appears on your credit card statement.
✅ How credit card rewards work ?
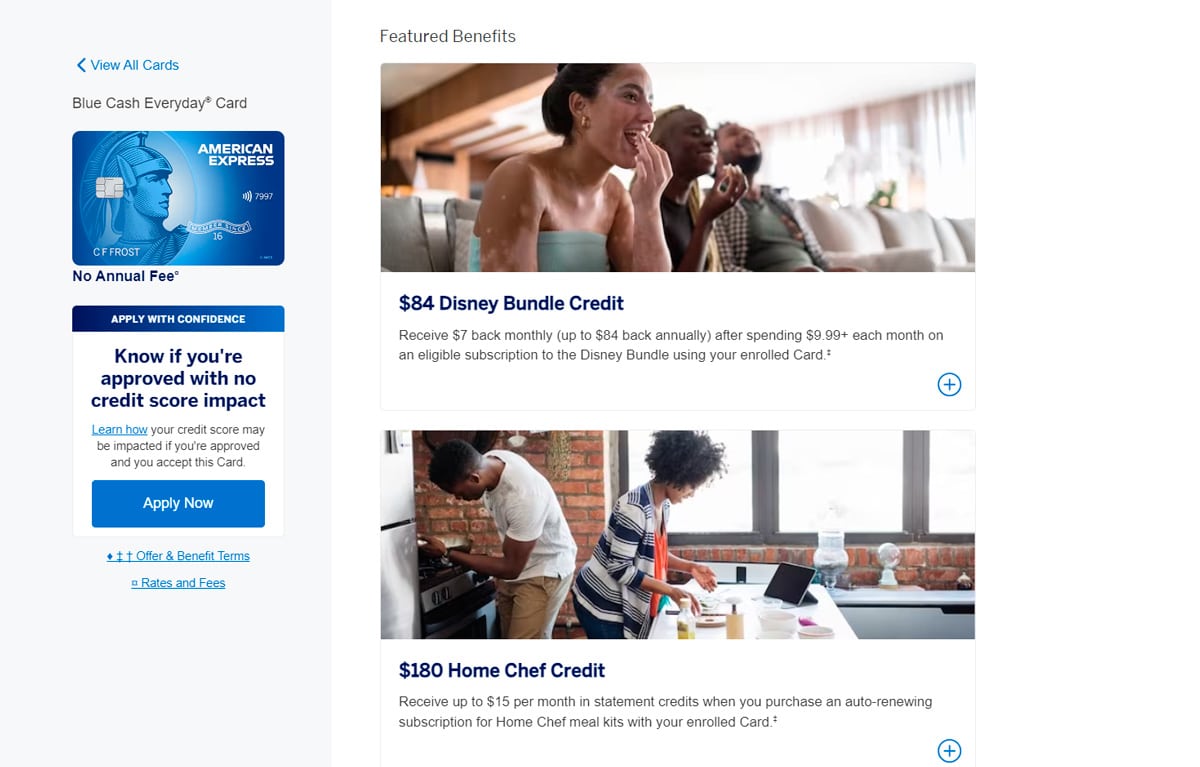
Credit card rewards are incentives provided by credit card issuers to encourage spending on their cards. These rewards are earned based on the amount you spend and can be accumulated as cash back, points, or miles, varying by the type of credit card and its reward scheme.
For instance, airline credit cards often reward purchases with miles that can be redeemed for airfare, while cash-back cards provide a return that can be applied as a credit to your statement or deposited directly into your bank account. General-purpose rewards cards might offer points that are redeemable for a wide range of options, including travel, merchandise, or other rewards.
Rewards structures can be uniform, offering a consistent percentage back on all purchases, such as a card that provides 2% back on every transaction. Alternatively, they can be tiered, offering higher reward rates on specific categories like gas or groceries compared to other types of spending. When selecting a rewards card, it's important to consider your spending patterns and which rewards will be most beneficial for you, comparing various options available in the market.
Rewards are typically categorized into:- Cash Back: Directly reduces your balance or can be received as a bank deposit or check.
- Points or Miles : Redeemable for travel, gift cards, merchandise, among other things, with some cards allowing points to be used as a credit on your statement, similar to cash back.
 Reward rates set by the issuer can be:
Reward rates set by the issuer can be:
- Flat Rate: A consistent reward rate for all spending.
- Bonus Rewards : Base rates for general spending with higher rates for specific categories, determined by the merchant's category code.
To maximize rewards, many users carry multiple cards, each offering bonus rewards in different categories, along with a flat-rate card for purchases outside those categories.
Tracking and redeeming rewards:- Rewards are stored in an account accessible through the issuer's online platform or mobile app.
- The process includes making a purchase, the issuer calculating and crediting rewards to your account, and you redeeming rewards through the online account. Redemption methods vary; cash-back is straightforward, while points or miles might require booking through an online travel portal.
Understanding and managing credit card rewards effectively requires familiarity with your card's rewards structure, regular tracking of earned rewards, and strategic redemption to maximize value.
✅ How Does Credit Card Interest Work ?
Credit card interest is a critical concept for users to grasp as it affects how much you end up paying when you carry a balance. Unlike some loans that calculate interest monthly, credit card interest is typically calculated daily, making understanding its workings vital for financial management.
Daily Calculation and Compounding- Daily Interest Rate : Credit card companies use your card's Annual Percentage Rate (APR) divided by 365 to determine a daily interest rate. This rate is then applied to the card's balance each day, leading to interest that compounds, meaning it builds upon itself.
Example of Calculation : If your credit card has a balance of $10,000 with an APR of 17%, the daily rate would be 0.0466% (17% / 365). Applied to the balance, it would result in a new balance of $10,004.66 the next day, demonstrating how compounding makes the debt grow.
APR vs. APY: Understanding the Differences- Annual Percentage Rate (APR): This is the yearly rate charged for borrowing on your credit card. It does not take into account the compounding of interest within the year, making it crucial for understanding the cost of borrowing.
- Annual Percentage Yield (APY) : Conversely, APY reflects the amount of interest one earns, considering compounding over the year. It's pertinent to savings, not borrowing.
- Interest Accumulation : If you do not pay your credit card balance in full each month, the interest will be calculated on the daily balances using the daily rate. This interest is then added to your balance, increasing the total amount you owe.
- Grace Periods : Many credit cards offer a grace period, allowing you to avoid interest charges by paying off your balance in full by the due date. If you carry a balance beyond this period, you will incur interest.
- Responsible Usage : To avoid being overwhelmed by interest and fees, it’s crucial to use credit cards responsibly. This means not spending more than you can afford to pay off each month and always making payments on time.
- Interest Rates and Your Credit : Generally, the better your credit score, the more favorable the interest rates you'll qualify for. However, credit card interest rates are often higher than those of other types of consumer debt, emphasizing the importance of careful credit card use.
In summary, understanding how credit card interest works, including how it's calculated, the difference between APR and APY, and how to manage your card responsibly, can help you avoid unnecessary charges and maintain financial health.
✅ How To Apply for a Credit Card ?
Applying for a credit card involves a series of steps designed to match you with a card that fits your financial situation and needs. Here's a streamlined guide to navigate this process:
1. Check Your Credit Score- Sources: Obtain your credit score through a credit card issuer's offer or by requesting it from one of the three major credit bureaus.
- Importance: Your credit score is a key factor in determining your eligibility for different types of credit cards.
- Categories: Credit cards can be broadly classified into rewards, low APR (Annual Percentage Rate), and credit-building cards.
- Selection Criteria: Choose based on your intended use, whether for earning rewards, saving on interest costs, or building or repairing your credit.
- Methods: You can apply online, over the phone with an agent, via a mailed paper application, or in person at a bank or financial institution.
- Application Information: Be prepared to provide personal details (name, address, contact information), financial information (employment, income, assets, debts), and identification numbers (Social Security number, birthdate) to process the application.
- Credit Check: The issuer assesses your creditworthiness by reviewing your credit report, not just your score, to understand your financial behavior and obligations.
- Decision Factors: Decisions are based on your credit history, application frequency, income, and debt-to-income ratio.
- Approval: If approved, most online applications yield instant decisions, while mailed applications may take longer.
- Receiving Your Card: Once approved, the credit card typically arrives within 10 business days.
- Activation: Activate your card by following the issuer's instructions, usually online or by phone, to start using it.
✅ Types of Credit Cards
Rewards Credit CardsRewards credit cards are designed to offer you benefits for your spending, returning a portion of your expenditures in the form of cash back, points, or miles.
The rate at which you earn these rewards can significantly differ across cards. Some cards provide a uniform rate on all purchases, while others feature tiered rewards systems, where specific categories of purchases, such as dining or travel, earn rewards at higher rates.
- 💸 Cash Back Credit Cards : These cards offer the simplest form of rewards by returning a percentage of your spending as cash. This cash can typically be applied as a credit to your statement, deposited into a bank account, or mailed to you as a check.
- 🌍 General Travel Credit Cards : Offering flexibility, these cards allow you to use the points you've earned to cover travel expenses. Unlike brand-specific travel cards, general travel credit cards let you redeem points across a wide range of airlines and hotels, providing freedom in how you choose to travel.
- ✈️ Airline Credit Cards : Tailored to frequent flyers of specific airlines, these cards enable you to earn miles for your spending that can be redeemed for flights and upgrades with the associated airline. Benefits often include airline-specific perks such as priority boarding and free checked bags.
- 🏨 Hotel Credit Cards : Similar to airline cards but for accommodation, these cards are linked to hotel chains, allowing you to earn points for stays and services. The perks of these cards often include free annual night stays, room upgrades, and elite status within the hotel's loyalty program.
A balance transfer credit card offers a strategic opportunity to manage and reduce debt more efficiently. These cards typically feature a low or 0% introductory Annual Percentage Rate (APR) on debt transferred to the card for a set period, often ranging from a year to over 18 months.
This introductory phase allows cardholders to pay down their transferred balances without accruing additional interest, providing a valuable window to reduce debt faster.
0% APR Credit CardsA 0% APR credit card provides a unique opportunity for users to enjoy an interest-free period on new purchases, balance transfers, or both, depending on the card's terms. Think of it as a temporary reprieve from interest charges, akin to an interest-free loan with an expiration date. During this introductory period, responsible usage allows cardholders to pay off their balances without incurring additional finance charges, providing a valuable window to manage debt effectively.
Low Interest Credit CardsLow interest credit cards provide a valuable option for individuals who anticipate carrying a balance on their cards over an extended period. Unlike limited-time 0% APR cards, low interest cards feature a consistently low ongoing interest rate, typically well below the industry average APR found on other credit cards. This makes them particularly advantageous for cardholders who expect to maintain a balance from month to month.
Student Credit CardsCollege student credit cards are essentially similar to other credit cards in terms of functionality and usage. However, they are specifically targeted towards college students or individuals with limited credit histories, who may encounter challenges in obtaining approval for a standard credit card
College student credit cards offer a tailored solution for individuals who are embarking on their credit journey. By providing accessible approval criteria and educational resources, these cards facilitate responsible credit usage and help students establish a solid foundation for their financial future.
Credit Cards To Build CreditFor individuals who are new to credit or aiming to recover from past credit challenges, there are specialized credit cards tailored to help demonstrate responsible payment behavior and enhance credit profiles. While credit cards offering premium rewards, perks, low interest rates, and extended 0% periods are typically reserved for those with good to excellent credit scores, there are options available for individuals in the process of building or rebuilding their credit.
Business Credit CardsUtilizing a business credit card can effectively delineate personal expenses from business-related ones, a particularly advantageous practice even for individuals engaged in part-time entrepreneurial ventures. While applying for a small business credit card, your approval hinges primarily on your personal credit score. Consequently, you assume personal liability for any incurred debts, even if they pertain to your business endeavors and subsequently encounter financial challenges. Moreover, the issuer evaluates additional factors such as your business income and credit history during the application review process.
✅ How to choose a credit card ?
Choosing the right credit card entails careful consideration of various factors tailored to your individual circumstances, ensuring optimal alignment with your financial goals and preferences.
Here's a comprehensive guide on how to select the most suitable credit card:
- Credit Score : Evaluate your credit score to ascertain your eligibility for different card options. Understanding your creditworthiness is crucial for identifying cards that match your financial profile.
- Annual Fee : Consider whether the benefits and rewards offered by a card outweigh its annual fee. While some cards offer rich rewards and perks in return for an annual fee, others may provide comparable benefits with no annual fee.
- Other Fees : Be mindful of additional fees associated with owning a credit card, such as balance transfer fees, foreign transaction fees, cash advance fees, late fees, and returned-payment fees. Choose a card with fee structures aligned with your spending habits and financial objectives.
- Interest Rates : Assess the APR (Annual Percentage Rate) of potential credit cards, particularly if you anticipate carrying a balance. Opt for cards with lower interest rates to minimize the cost of carrying debt over time.
- Rewards : Select a card with rewards programs that complement your spending habits and lifestyle preferences. Evaluate factors such as earn rate, redemption value, and flexibility in reward redemption options.
- Sign-up Bonus : Look for cards offering enticing sign-up bonuses or welcome offers, which can provide significant value in the initial months of card ownership.
- Perks : Assess the perks and benefits offered by different cards, including travel benefits, purchase protections, rental car coverage, statement credits, and credit tracking/security features. Choose cards that offer perks aligned with your spending priorities and lifestyle needs.
- Credit-Building Help : For individuals looking to build or improve their credit, prioritize cards that report to credit bureaus, offer incentives for responsible behavior, and provide opportunities for credit line upgrades.